Amenhotep II, the seventh pharaoh of Egypt’s 18th Dynasty, reigned during a pivotal period in ancient Egyptian history. His legacy as a powerful ruler and his well-preserved mummy continue to fascinate historians and enthusiasts alike.
The Reign of Amenhotep II
Amenhotep II’s reign was marked by military campaigns, architectural achievements, and the consolidation of power.
Royal Lineage and Succession
Amenhotep II’s lineage and succession played a crucial role in shaping his reign and legacy.

- Son of Thutmose III:
- Amenhotep II was the son of the renowned pharaoh Thutmose III, inheriting a powerful and prosperous kingdom.
- His father’s military campaigns and administrative reforms laid the foundation for his own reign.

- Father of Thutmose IV:
- He was also the father of Thutmose IV, ensuring the continuation of the 18th Dynasty’s rule.
- His descendants continued to shape Egypt’s history for generations.

- Grandfather of Amenhotep III:
- As the grandfather of Amenhotep III, he was part of a lineage of powerful pharaohs who left a lasting impact on Egypt.
- His influence extended beyond his own reign, shaping the future of the kingdom.
Military Campaigns and Consolidation
Amenhotep II was known for his military prowess, leading campaigns to secure Egypt’s borders and consolidate his power.
- Military Prowess:
- He was a skilled military leader, continuing his father’s legacy of expansion and control.
- His campaigns aimed to maintain Egypt’s dominance in the region.
- Consolidation of Power:
- Amenhotep II focused on consolidating his power and ensuring stability within the kingdom.
- His policies aimed to strengthen the central government and maintain control over conquered territories.
- Strategic Campaigns:
- His military campaigns were strategically planned and executed, demonstrating his leadership and tactical skills.
- He ensured that Egypt remained a formidable power in the ancient world.
Architectural Achievements
Amenhotep II contributed to Egypt’s architectural legacy, leaving behind monuments and structures that reflect his reign.
- Karnak Temple:
- He made significant contributions to the Karnak Temple complex, adding to its grandeur and religious significance.
- His additions reflected his devotion to the gods and his commitment to maintaining Egypt’s religious traditions.
- Valley of the Kings:
- His tomb in the Valley of the Kings (KV35) is a testament to the architectural and artistic achievements of the 18th Dynasty.
- The tomb’s design and decoration reflect the pharaoh’s status and beliefs about the afterlife.
- Monumental Structures:
- He commissioned the construction of various monumental structures, showcasing his power and wealth.
- These structures served as symbols of his reign and his connection to the divine.
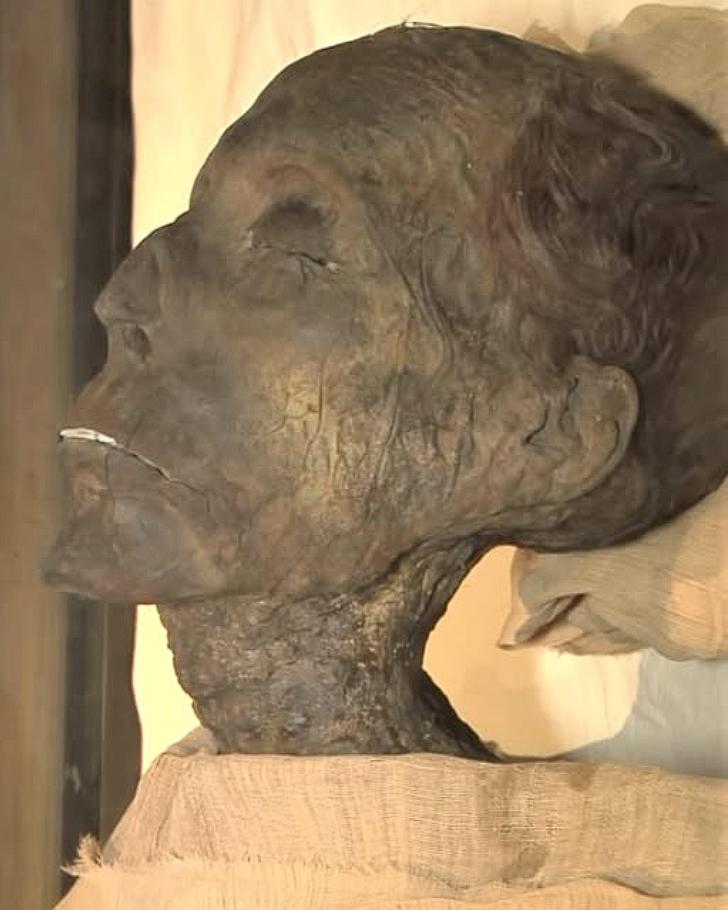
The Discovery and Analysis of His Mummy
The discovery and analysis of Amenhotep II’s mummy have provided valuable insights into his life, health, and the mummification practices of the time.
Discovery in KV35
The discovery of Amenhotep II’s mummy in his tomb (KV35) in the Valley of the Kings was a significant archaeological event.
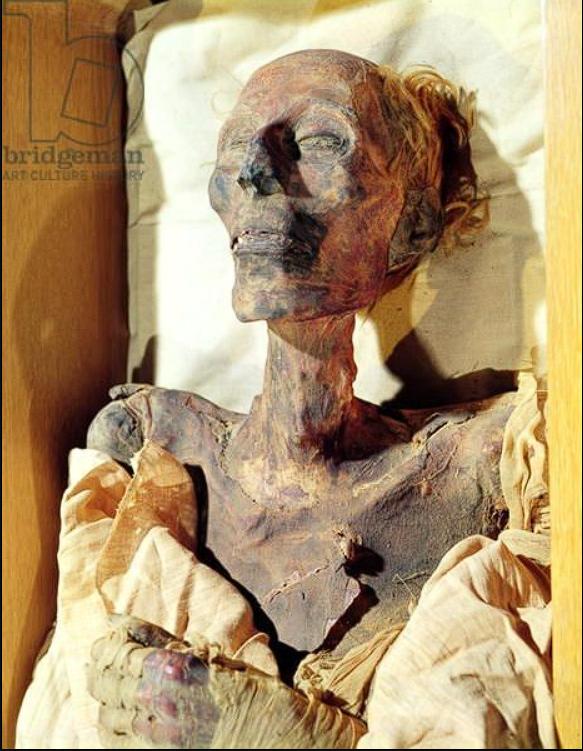
- Victor Loret’s Discovery:
- French excavator Victor Loret discovered the mummy of Amenhotep II in 1898, still resting in his original sarcophagus.
- This discovery was a remarkable find, providing a rare glimpse into the burial practices of Egyptian pharaohs.
- Undisturbed Sarcophagus:
- Before the discovery of Tutankhamun’s tomb, Amenhotep II was the only king whose mummy had survived intact in his sarcophagus.
- This made his discovery particularly significant for understanding ancient Egyptian burial customs.
- Valley of the Kings:
- The location of his tomb in the Valley of the Kings highlights the importance of this site as a royal burial ground.
- The discovery added to the site’s historical and archaeological significance.
Analysis by Sir Grafton Elliot Smith
Sir Grafton Elliot Smith’s analysis of Amenhotep II’s mummy in 1907 provided valuable insights into the pharaoh’s health and physical characteristics.
- Skin Bumps:
- Smith discovered small bumps on the king’s skin, the origin of which remains uncertain.
- These bumps could be due to the mummification process or a pre-existing condition.
- Resemblance to Thutmose IV:
- Smith noted a strong resemblance between Amenhotep II and his son, Thutmose IV.
- This observation highlights the familial traits and genetic connections within the royal lineage.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Smith’s analysis provided insights into the king’s physical characteristics, including his hair color and age at death.
- These details contribute to our understanding of Amenhotep II as a historical figure.
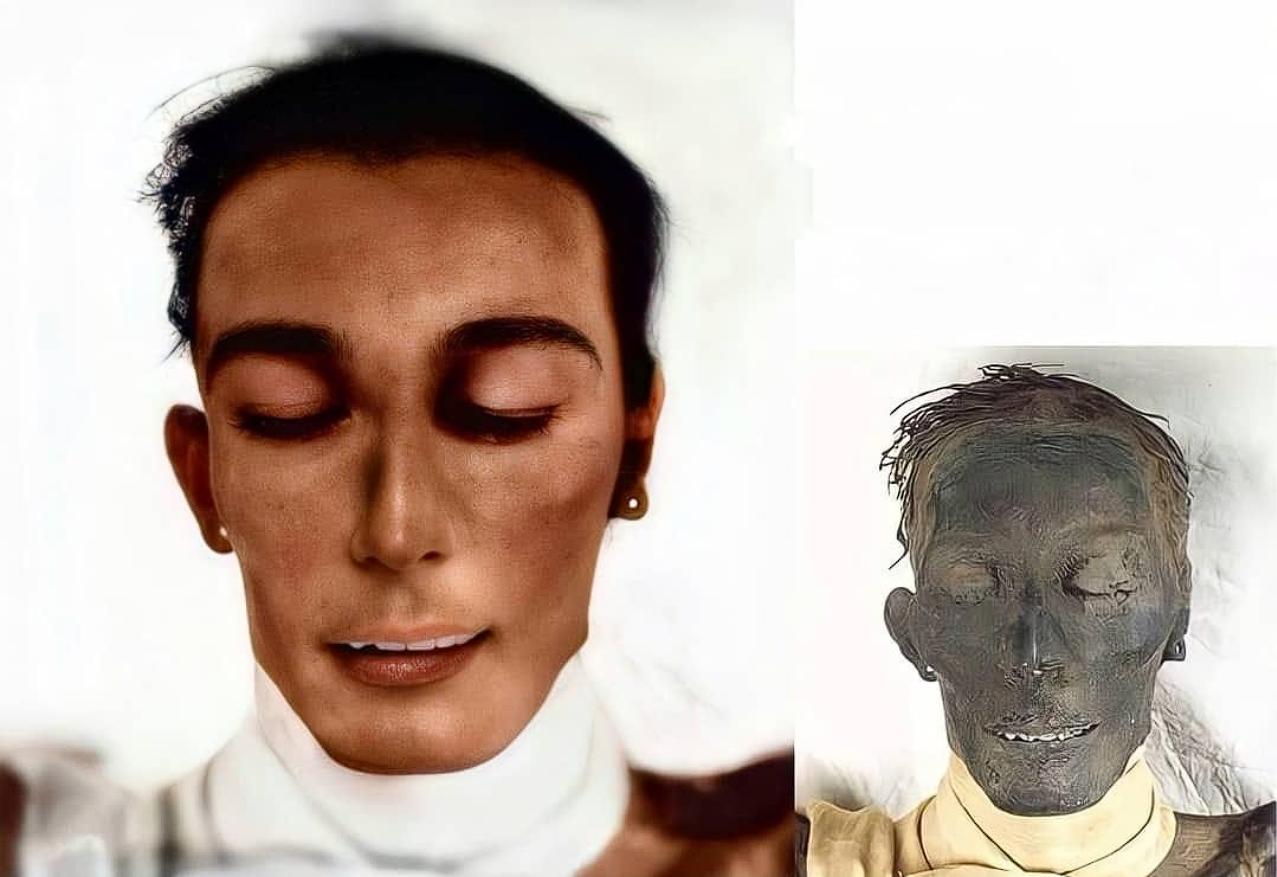
Insights from Dr. Joann Fletcher
Dr. Joann Fletcher’s research has provided further details about Amenhotep II’s life and physical condition.
- Middle-Aged at Death:
- According to Fletcher, Amenhotep II was middle-aged when he died, with his hair showing signs of graying.
- This detail adds to our understanding of the pharaoh’s age and physical condition at the time of his death.
- Wavy Brown Hair:
- Fletcher’s research confirms that Amenhotep II had wavy brown hair, providing a glimpse into his appearance.
- This detail helps to humanize the pharaoh and connect him to our understanding of ancient Egyptian society.
- Chronicle of a Pharaoh:
- Fletcher’s book, “Chronicle of a Pharaoh, The Intimate Life of Amenhotep III,” provides valuable insights into the lives of Egyptian pharaohs.
- Her research contributes to our understanding of ancient Egyptian history and culture.
Amenhotep II’s reign and his well-preserved mummy continue to fascinate historians and enthusiasts, providing valuable insights into ancient Egyptian history and culture. His legacy as a powerful pharaoh and his enduring presence through his mummy make him a significant figure in the study of ancient Egypt.
