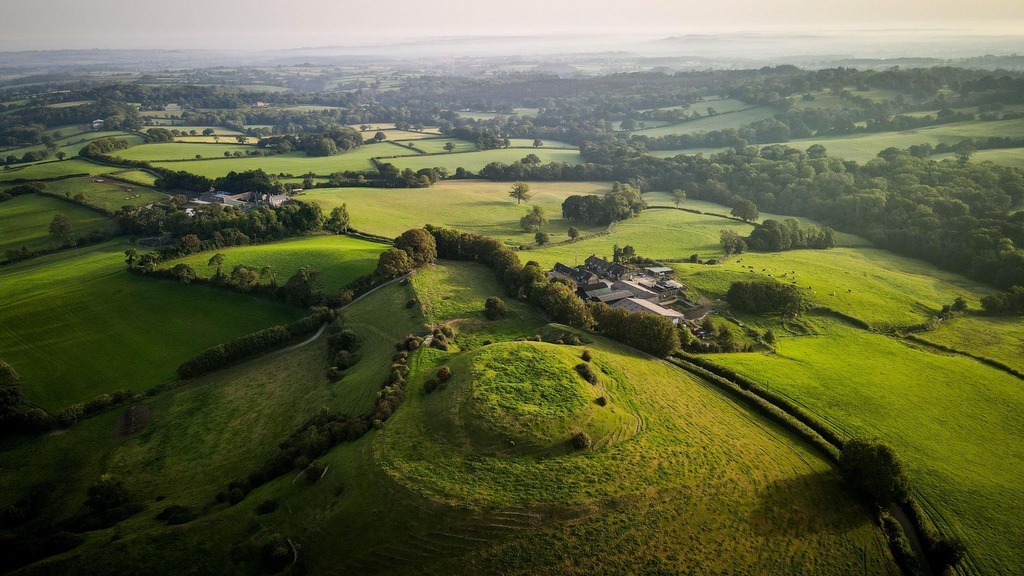
Castle Hill, with its well-preserved motte and bailey structure, stands as a powerful reminder of Norman conquest and medieval military strategy. This site, located in East Chelborough, Dorset, offers a glimpse into the era of William the Conqueror and the consolidation of Norman control.
The Strategic Design of Motte and Bailey Castles
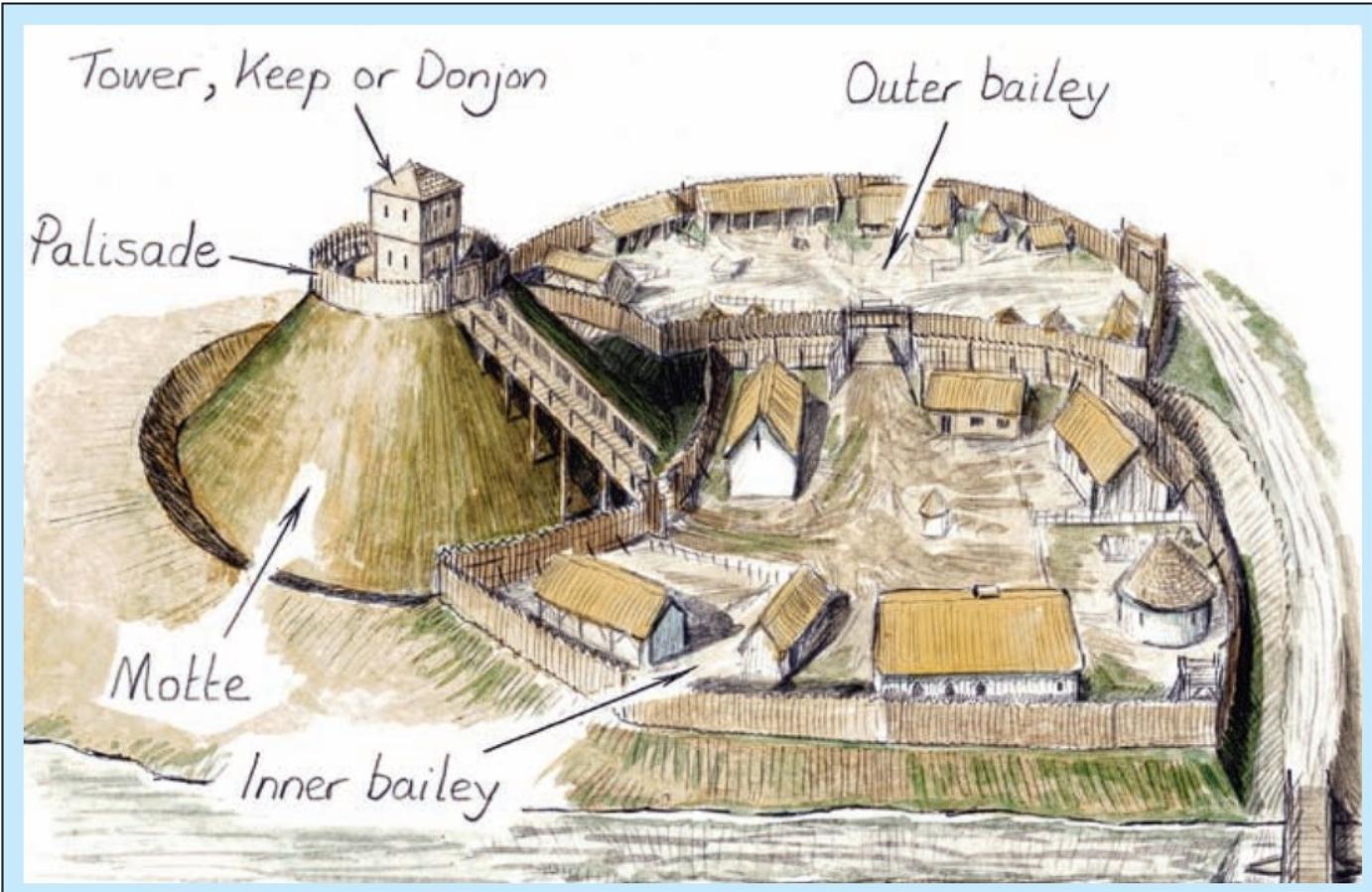
Motte and bailey castles, like Castle Hill, were strategically designed to serve multiple purposes, from military strongholds to administrative centers.
Garrison and Stronghold
These castles acted as garrison forts during offensive military operations, providing secure strongholds for Norman forces.

- Offensive Operations:
- Motte and bailey castles served as crucial staging points for offensive military operations, allowing Norman forces to project power into surrounding territories.
- They were a key part of military strategy.
- Defensive Strongholds:
- They also functioned as defensive strongholds, providing secure bases for Norman garrisons and protecting newly acquired lands.
- They offered protection.
- Strategic Positioning:
- The strategic positioning of these castles, often on elevated ground, allowed for effective surveillance and control of the surrounding area.
- They had a tactical advantage.
Aristocratic Residence and Administration
Motte and bailey castles served not only as military installations but also as aristocratic residences and centers of local or royal administration.
- Aristocratic Dwellings:
- Many motte and bailey castles served as residences for Norman aristocrats, symbolizing their power and authority.
- They were places of power.
- Administrative Centers:
- They also functioned as centers of local or royal administration, facilitating the consolidation of Norman control and governance.
- They were places of government.
- Symbol of Authority:
- These castles served as potent symbols of Norman authority, reinforcing their dominance over the conquered population.
- They were a symbol of control.
Construction and Military Formidability
Motte and bailey castles were relatively straightforward to construct using unskilled labor, yet remained militarily formidable.

- Simple Construction:
- The construction of these castles, typically involving a wooden or stone keep on a “motte” and a walled “bailey,” was relatively simple and efficient.
- They were quick to build.
- Defensive Features:
- Defensive features, such as ditches and palisades, complemented the keep and bailey, enhancing the castle’s military strength.
- They were strong defensive structures.
- Military Effectiveness:
- Despite their simplicity, motte and bailey castles proved to be highly effective military structures, contributing to the success of the Norman conquest.
- They were very effective.
Castle Hill’s Historical Significance
Castle Hill’s strategic position and architectural features highlight its pivotal role in the Norman conquest and subsequent control of the region.
Commanding the Landscape
Castle Hill’s elevated position and commanding view of the surrounding landscape underscore its strategic importance.
- Dominating Locality:
- The castle’s position allowed it to dominate the immediate locality, providing a clear view of approaching forces and potential threats.
- It had a clear view.
- Visual Impression:
- As a result, motte and bailey castles like Castle Hill are the most visually impressive monuments of the early post-Conquest period surviving in the modern landscape.
- They are impressive to see.
- Saxon Impact:
- The castle’s imposing presence would have commanded the attention of the Saxons, symbolizing the Norman conquest and the shift in power.
- They would have been awed.
Norman Conquest and Control
William the Conqueror’s strategic use of motte and bailey castles played a crucial role in consolidating Norman control over England.
- Strategic Fortification:
- William the Conqueror constructed motte and bailey castles strategically, fortifying crucial positions to solidify his control over newly acquired lands.
- They were key to his strategy.
- Consolidation of Power:
- These castles played a pivotal role in ensuring the Normans’ triumphant conquest of the British Isles, establishing their dominance.
- They helped him win.
- Pivotal Role:
- The castles played a pivotal role in the Norman’s triumphant conquest.
- They were essential.
East Chelborough’s Historical Setting
Castle Hill at East Chelborough, Dorset, evokes images of Norman knights planning their conquest and solidifying their control over the region.
- Norman Knights’ Planning:
- The site evokes images of Norman knights planning their next operations, strategizing how and where they would fight the next battles.
- It is a place of history.
- Pushing West:
- The castle’s location suggests its role in the Norman advance westward, subduing the Saxons and expanding their territory.
- It was a part of the push.
- Evocative Setting:
- The gorgeous piece of history still sits at East Chelborough, providing an evocative setting for imagining the Norman conquest.
- It is a beautiful and historical location.
Castle Hill stands as a testament to the strategic brilliance and military effectiveness of motte and bailey castles, playing a crucial role in the Norman conquest and the reshaping of the English landscape. Its enduring presence in East Chelborough, Dorset, continues to captivate and educate visitors about this pivotal period in history.
